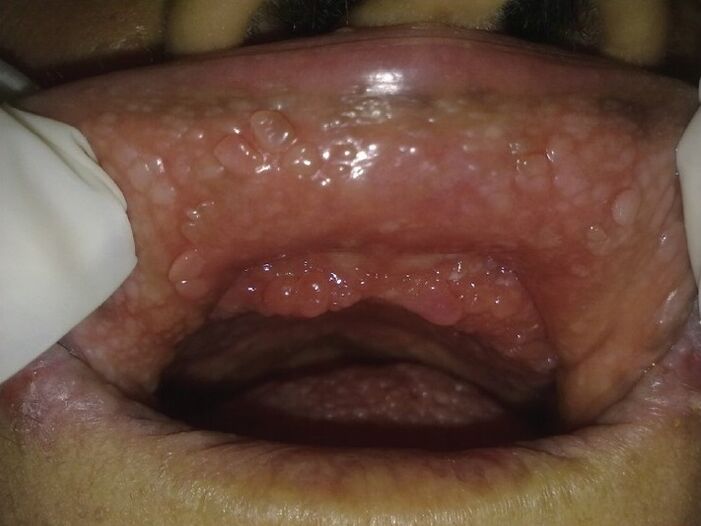
Papillomas (or warts) are uncommon in men.
Usually they do not cause pain, but they require treatment because they are a threat to their owner and those around him.
what is it
Papillomas are growths that form as a result of excessive division of skin or mucosal epithelial cells.
Its emergence is caused by papillomaviruses - which alter the DNA of human cells, causing them to multiply in abundance.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is an extremely common microorganism.
It has been established that approximately half of adults are carriers of one or the other strain or have clinical manifestations of the disease.
Thanks to active immune protection, a person can face the virus every day without getting sick. But reduced resistance makes the body vulnerable.
To date, more than 100 HPVs have been identified.
What a papilloma on the skin looks like: treatment and prevention of papillomavirus infection
The external manifestation of human papillomavirus is papilloma on the skin. Tumors, often called warts, are benign in nature. But seemingly harmless growths can develop malignancies and transform into cancerous tumors.
Why do papillomas appear on the skin?
You can contract the virus through contact with someone who is a carrier of the strain or through household contact while using contaminated items.
In newborns, the cause of papillomatosis is through the mother's infected birth canal.
HPV infection can also occur under the influence of the following adverse factors:
- weakened immune system;
- having sex with an unproven partner;
- bad habits;
- long-term treatment with certain medicines;
- Depressive tendencies;
- infectious diseases;
- Hygiene regulations are not followed in public places with high humidity.
When HPV (the main cause of cutaneous papillomas) enters the body, it affects the basal layer where the epithelium transitions from multilayer to cylindrical. As a result, the infected cell becomes benign, but it is then able to regenerate and trigger mechanisms for cancer development.
A pedunculated tumor deserves special attention—because it is easily injured, it can infect surrounding healthy surfaces and cause multiple papillomatosis.
Warts don't always turn into tumors. If they are caused by viruses with low carcinogenicity, you don't need to worry. These are strains 42, 44, 11 and 6. A dermatologist or venereologist can determine the extent of cancer risk.
Diagnosis of papillomatosis
What do papillomas look like on the skin? Standard options are rough, soft growths that look like mushroom or cabbage inflorescences. Its size can reach 2 cm.
Tumors are of the following types:
- Simple - These are rough growths that start at 1mm in size. They tend to pack into arrays under a single cuticle. This papilloma forms under the knees, on the backs of the fingers and palms.
- Plantar warts, similar to calluses, form as small, shiny bumps. Over time, they grow and feature prominent edges. Branches separate from the main growth in the form of smaller childhood warts.
- Filamentous growths resemble elongated tapered rods that reach 6 mm in length.
- Flat tumors are characterized by the body's natural shading and resemblance to flattened cones. If they are present, people complain of itching, and occasionally - redness in focus.
- Genital warts are tumors that appear on both male and female genitals. They affect the skin and mucous membranes. The color of condyloma acuminatum is flesh color, pink, red. Sizes vary from 1mm to a few centimeters.
After a visual examination of the patient, a specialist will recommend him to perform a PCR diagnosis of viral DNA. Based on his answers, doctors will be able to determine the type, carcinogenicity and number of strains. PCR can also give you an idea of whether papillomatosis is chronic or abrupt on the background of a dramatic decline in immunity.
Microscopic preparations of cutaneous papillomas are represented by connective tissue stroma and epithelium. The nature of the latter determines the type of tumor, namely squamous and transitional cells. The connective tissue of the stroma is defined as dense or loose. Usually it becomes edematous, inflamed and filled with blood vessels. In the case of growth sclerosis, a diagnosis of fibrosing papilloma is made.
The epithelial layer covering the wart shows an increase in the number and size of pathological cells. This indicates hyperkeratosis. The histological structure of papillomas may differ from one another.
For example, areas of parakeratosis and vacuolar epithelial cells are inherent in common cutaneous papillomas. In senile keratoses, formation with epithelial cell polymorphisms has been identified. In ICD 10, cutaneous papillomas are recorded under code B97. 7 "Papillomavirus as a cause of disease classified elsewhere".
Treatment and prevention of human papillomavirus infection
HPV treatment options are always chosen individually by the doctor. If the virus is detected before its clinical manifestation, the patient is offered the use of cytostatics.
Depending on the specific symptoms and localization, cutaneous papillomas are treated according to one of the following methods:
- Freeze destruction;
- radio wave therapy;
- electrocoagulation;
- laser evaporation;
- chemical damage.
Warts with signs of regression require surgery to remove and capture healthy tissue. After the external signs of carrying papillomavirus had been eliminated, the patient was prescribed antiviral therapy and had regular check-ups.
As a conservative treatment, drugs are prescribed that suppress the activity of the virus and strengthen the body's defenses.
The drug is released as a spray and is a topical preparation. Its use has antiviral and immunomodulatory effects. The spray is included in the comprehensive treatment of condyloma acuminatum.
There are several directions for preventing HPV infection. An important part of this is sex education for young people and explaining the characteristics and protection methods of viral transmission. Pay special attention to a healthy lifestyle, the development of stress resistance, and prompt treatment of any contagious disease.















